Early days and achievements
Born on August 1, 1968, in Virginia, United States, Woodriff exhibited early signs of brilliance and a passion for technology. He pursued his interest in computer science at the University of Virginia, where he graduated with a Bachelor of Science degree in 1991. Armed with his education, Woodriff embarked on his professional career as a software developer at IBM, laying the foundation for his future endeavors.
Woodriff's rise to prominence was marked by several notable milestones. In August 1994, he embarked on his trading journey with $50,000 invested by supportive friends and family. Subsequently, he sought employment as a proprietary trader in New York, finding an opportunity at Société Générale, where he honed his skills for two years. During this time, Woodriff refined a trading system he had initially developed right after graduating from the University of Virginia.
As the program began demonstrating exceptional performance, he made the pivotal decision to transition from managing others' funds to focusing on his own capital, which amounted to $300,000 at the time.
In 2003, Woodriff took a leap of faith and founded Quantitative Investment Management (QIM), a hedge fund that would reshape the industry. QIM differentiated itself by employing quantitative trading strategies and leveraging computer algorithms to drive investment decisions. This innovative approach, rooted in systematic trading, harnessed advanced mathematical models and statistical analysis to identify lucrative market trends and opportunities. Guided by Woodriff's vision and leadership, QIM swiftly emerged as one of the largest and most successful hedge funds worldwide.
Woodriff's influence extended beyond the establishment of QIM. Renowned for his commitment to data-driven decision-making, he became a driving force behind the application of cutting-edge technology and mathematical models in the finance field. His revolutionary mindset transformed the landscape of hedge fund operations, setting new standards for efficiency and performance.
Woodriff's trading prowess became evident through remarkable achievements. Between 2003 and 2011, QIM delivered an average annual compound return of 12.5% with a standard deviation of 10.5% for its clients.
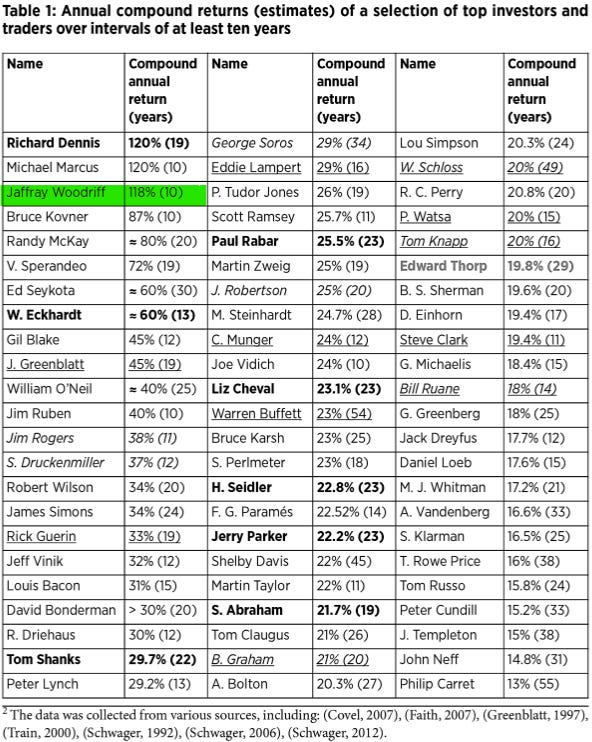
Notably, Woodriff's personal account, dedicated to trading Futures, achieved an astonishing average annual compound return of 118% with a standard deviation of 81%. These exceptional results propelled QIM's growth, with the firm currently managing an impressive $1.1 billion in assets.
Quantitative Investment Management
Jaffray Woodriff has gained recognition for his unconventional approach to computerized trading. Unlike many traders who rely on trend-following or mean-reversion strategies, Woodriff utilizes a pattern-recognition approach. His upbringing on a farm instilled in him a strong work ethic and a belief in the power of incentives, which is reflected in his firm's unique fee structure based solely on performance.
The inception of QIM is rooted in the failure of Woodriff Trading where he faced difficulties in raising assets and managing the business. Despite contemplating leaving the finance industry, he was convinced by a friend to continue trading. Woodriff's trading prowess was evident as he achieved success trading for a proprietary account before co-founding QIM with Michael Geismar and Greyson Williams.
QIM
QIM's trading programs, focused on futures and equity markets, have demonstrated impressive return/risk performance. Woodriff acknowledges the crucial role played by his co-founders and the dedicated staff at QIM. Despite his accomplishments, he remains humble and continuously seeks knowledge through extensive reading.
Woodriff's interest in computerized trading systems developed at a young age, driven by his fascination with odds, probability, and computers. His early experiences with dice and his first computer, a Commodore, sparked his passion for incorporating technology into trading.
Woodriff made significant breakthroughs in predictive modeling and trading strategies, initially testing separate models for each market. However, he realized that employing multiple models across various markets yielded better results than relying on a single best model.
Over time, Woodriff refined his trading approach. He transitioned from market-specific models to universal models applicable to all markets, leading to improved performance and robustness. As assets under management grew, he also increased diversification by trading in more markets.
The Approach
The key to Woodriff's success lies in his unique system concepts. Instead of adhering to common trend-following or mean-reversion strategies, he focused on identifying consistent systems that worked across markets. He derived secondary variables from daily price data, such as measures of volatility, and combined them into trend-neutral models. His system comprises over a thousand models, each predicting market direction over the next 24 hours.
Woodriff's discovery process involved searching for patterns in the data, deviating from the conventional approach of formulating hypotheses based on market theory.
He embraced the challenge of analyzing vast amounts of data, leveraging computational power and rigorous validation methods to avoid overfitting.
While much of the process is automated, the selection of meaningful secondary variables remains a manual task.
‘The majority of futures traders, called CTAs, use trend-following methodologies. These programs seek to identify trends and then take a position in the direction of the trend until a trade liquidation or reversal signal is received.
A smaller number of systematic CTAs will use countertrend (also called mean reversion) methodologies. As the name implies, these types of systems will seek to take positions opposite to an ongoing trend when system algorithms signal that the trend is overextended.
There is a third category of systematic approaches whose signals do not seek to profit from either continuations or reversals of trend. These types of systems are designed to identify patterns that suggest a greater probability for either higher or lower prices over the near term. ‘
-Market Wizards
Woodriff is among the small minority of CTAs who employ this last pattern-recognition approach, and he does so using his own unique methodology. He is one of the most successful practitioners of systematic trading of any kind.
10 Key lessons
Analyzing the interview Jaffray gave to Jack Schwager for his chapter in the Hedge Fund market wizards, I found 10 specific lessons I would like to share with you.
Data Weighting
Woodriff acknowledges the value of older data, stating that patterns uncovered from the 1980s are still remarkably useful. While some weight is given to more recent data, he emphasizes the stationarity of patterns in markets over the long term.
Model Performance
QIM does not react to short-term model results. Instead, they assess performance over the entire training period, typically 31 years, to determine whether a model should be dropped. Woodriff highlights that a single year's performance is not predictive of future performance.
Capacity and Market Allocation
QIM has made changes to accommodate larger assets under management. They execute trades throughout the trading session, allocate a greater percentage to more liquid markets like stock indexes and interest rates, and reduce allocation to nonfinancial futures contracts. These adjustments have expanded capacity and improved performance.
Risk Control
QIM evaluates the risk of each market based on an exponentially weighted moving average of the daily dollar range per contract. This risk management metric helps maintain volatility close to the target level even during periods of market gyrations.
Leverage Reduction
Woodriff discusses their leverage reduction policy, which aimed to reduce exposure after drawdowns. However, he notes that during certain periods, the policy adversely impacted performance when the models performed exceptionally well during reduced exposure.
Trading Systems
Jaffray's success provides insights into trading systems. He highlights the possibility of finding systems that work better than trend following or countertrend approaches. He also mentions the cautious use of data mining techniques to identify useful patterns and the importance of designing systems that work broadly across multiple markets.
Risky Misconceptions
Woodriff criticizes the unregulated and opaque nature of over-the-counter (OTC) markets, highlighting the need for fair and transparent markets. He also mentions that overtrading and reliance on tips are common mistakes made by the public in financial markets.
Emotional Strain and Improvement
Woodriff acknowledges that periods of poor performance are difficult but focuses on improving the trading system during such times.
Trading Rules
Woodriff's trading rules include looking where others don't, adjusting position sizes to manage overall risk and target specific volatility.
Personal Discipline and Progress Evaluation
Woodriff credits his father for instilling in him the discipline of objectively evaluating his progress, which has been critical to his success.
Final words
In conclusion, Jaffray Woodriff's journey in the world of finance and systematic trading stands as a testament to his visionary approach, unwavering dedication, and relentless pursuit of innovation. From his humble beginnings as a software developer at IBM to the founding of Quantitative Investment Management, Woodriff has consistently pushed the boundaries of what is possible in the field of computerized trading.
By leveraging advanced mathematical models, cutting-edge technology, and a pattern-recognition approach, Woodriff revolutionized the industry and achieved extraordinary results. The success of Quantitative Investment Management, with its impressive track record, is a testament to Woodriff's trading prowess.
Beyond his personal achievements, Woodriff has left an indelible mark on the hedge fund landscape through his specific approach to the markets
Let us soon dig into Jim Simons journey to compare commonalities and differences between these two mathematical quant investors.